- Written by: vkaladigitalsolutions07@gmail.com
- July 21, 2025
- Categories: Uncategorized
- Tags:
Table of Contents
ToggleGuide for SEO in 2025
SEO is changing fast, and 2025 brings new rules to the game. Search engines are getting smarter, and just stuffing keywords won’t work anymore. This guide will help you understand what really matters now—like writing helpful content, making your website easy to use, and keeping up with Google’s latest updates. You’ll learn about new trends like voice search, AI tools, and how to show up even when there’s no click. Whether you’re running a business or just starting out with SEO, this guide breaks it all down in a simple, clear way so you can grow your online presence with confidence.
Understanding Search Engine
- Introduction to Search Engines
- Crawling to Indexing: The Search Engine Process
- Why Some Pages Show Up First on Google
- Search Personalization Explained Simply
Introduction to Search Engines
Search engines are tools that help you find information on the internet. Whether you’re looking for a recipe, news article, or a nearby café, search engines like Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo scan the web to deliver relevant results instantly.All you have to do is type in a query, and within seconds, you’re shown a list of links, images, and videos that match what you’re looking for.
Behind the scenes, search engines use complex algorithms to understand what your query means and where to find the best possible answers. They sift through billions of web pages, rank them based on relevance and quality, and present the top matches on a results page. This process is fast, efficient, and continuously evolving as technology advances.
How do search engines make money?
1.PAY-PER-CLICK ADs- Search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo primarily make money through advertising, specifically a model called Pay-Per-Click (PPC). Businesses bid on keywords to show their ads at the top of search results, and each time someone clicks on one of these ads, the business pays a small fee to the search engine. These are known as paid results or sponsored listings, and they are usually labeled as “Ad” at the top of the search results page.

Organic Search—In contrast, the organic results that appear below the ads are not paid for — they are ranked based on relevance and quality using complex algorithms. While these don’t directly earn money, search engines work to make them highly useful so that users keep coming back. The more searches people do, the more chances there are for ads to be shown — and clicked — making advertising the core business model for most search engines.
Crawling to Indexing: The Search Engine Process
The first step in a search engine’s job is crawling. This means it sends out tiny bots—called “web crawlers” or “spiders”—that browse the internet and discover new or updated pages. These bots follow links from one page to another, gathering data as they go. They don’t see web pages like humans do; instead, they scan the code and structure to understand what each page contains.
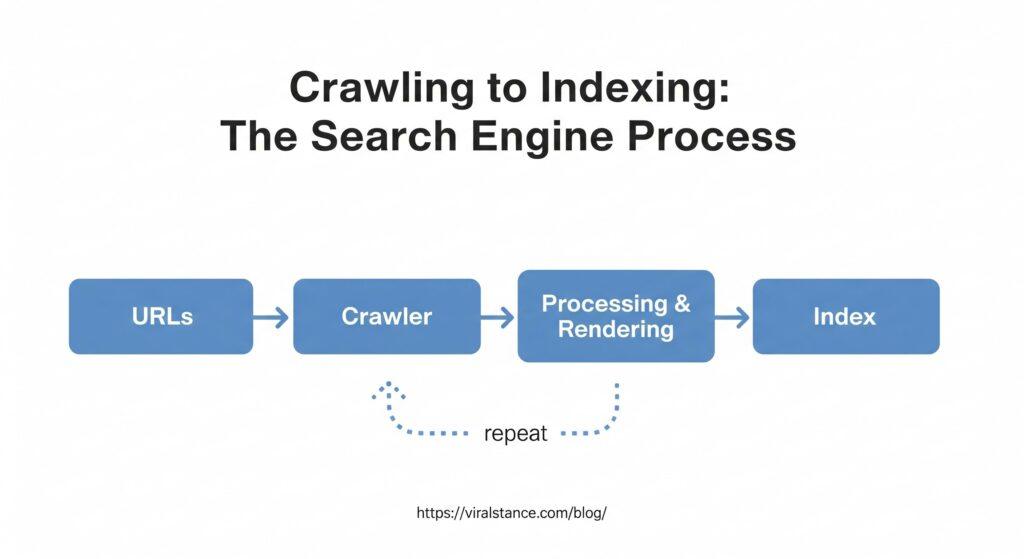
1. URLs
The process begins with a list of URLs—web addresses that the search engine wants to visit. These can come from sitemaps, backlinks, or previous crawls.
2. Crawling
Search engine bots, called crawlers or spiders, visit these URLs to discover content on the web. They follow links and gather page data as they go.
3. Processing & Rendering
Once pages are crawled, the search engine processes the content, executes any code (like JavaScript), and understands the structure of each page.
4. Indexing
After rendering, the page content is stored in a massive database called the index. This allows the search engine to quickly find and rank relevant pages for users’ queries.
Once a page is crawled, the search engine moves to the indexing phase. This is where the information collected by the crawlers is organized and stored in a massive database called the search index. Think of it like a library catalog for the web. If a page isn’t in the index, it won’t appear in search results—no matter how great the content is.
Why Some Pages Show Up First on Google
Not all web pages are treated equally by search engines. When you search for something, Google uses an algorithm to decide which pages are most relevant and useful to your query. Factors like page content, keyword usage, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and quality of backlinks all play a role in determining a page’s rank.
The higher a page appears in the search results, the more likely people are to click on it. That’s why businesses invest in SEO (Search Engine Optimization) — a set of practices designed to improve their website’s visibility in search. The goal is to meet search engine criteria so that the page ranks higher and reaches the right audience more effectively.
What Are Search Algorithms?
Search algorithms are step-by-step formulas that help Google find and rank the most relevant results from its database. Google looks at many things to decide which pages should appear first..
Google Ranking Factors
No one knows all the factors Google uses to rank pages, because Google hasn’t shared them all. But some important ones are known. Let’s check out a few of them.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites that point to your site. Google sees them as “votes of confidence.” The more high-quality backlinks you have, the more authority your site gains in Google’s eyes. However, quality matters more than quantity—links from trusted, relevant websites are more valuable than random or spammy ones.
Building backlinks through guest posting, partnerships, and shareable content is a powerful way to improve your search engine rankings.

Relevance
Google aims to show results that match a user’s intent. That’s why relevance is key. Your content must align closely with the search query—using clear headings, relevant keywords, and meaningful answers. Pages that directly answer users’ questions tend to perform better in search results.
To boost relevance, focus on structured content, long-tail keywords, and covering your topic thoroughly and clearly.
Freshness
Freshness refers to how recent or updated your content is. For certain search queries—like news, trends, or time-sensitive topics—Google prioritizes fresh content. Updating older blog posts and publishing regularly can help maintain content freshness.

Search engines want to serve users the most up-to-date information, so maintaining a content calendar and refreshing old pages is smart SEO practice.
Page Speed
Page speed is a ranking factor that impacts both SEO and user experience. Slow-loading pages can lead to higher bounce rates and lower engagement. Google recommends loading your site in under 3 seconds for the best results.

Search engines want to serve users the most up-to-date information, so maintaining a content calendar and refreshing old pages is smart SEO practice.
Mobile-Friendliness
With the majority of searches now happening on mobile devices, Google gives priority to mobile-friendly websites. Your site should be responsive, easy to navigate on small screens, and have fast mobile load times.
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to ensure your site meets the required standards. A mobile-optimized website not only ranks better but also keeps users happy and engaged.Search engines want to serve users the most up-to-date information, so maintaining a content calendar and refreshing old pages is smart SEO practice.
Search Personalization Explained Simply
Search engines don’t always show the same results to everyone. If two people search for “best pizza near me,” they might see completely different results based on their location, search history, language, and device. This is called search personalization, and it helps tailor the results to what’s most relevant for each individual.
Search engines use data—like your past searches, clicked links, or even the time of day—to predict what you’re most likely looking for. While this improves convenience and accuracy, it also raises privacy questions. That’s why some users prefer private search engines that don’t track or personalize their results.
Location
Search engines use your location to show results that are relevant to where you are. For example, searching “coffee shops” will display nearby cafés, helping users find local services quickly.
Search History
Search engines consider your past searches to offer more personalized and relevant results. It helps in predicting what you’re looking for based on your browsing behavior.

Language
Language settings help search engines deliver results in the language you understand best. This ensures clearer content and better user experience based on your preferences.
Key-takeaway
Google personalizes results by language, showing content in the user’s preferred or browser-set language.
Location and regional targeting influence which version of a page ranks higher in a specific country.
Multilingual SEO is essential for reaching a global audience effectively.
Content should be localized, not just translated, to match regional intent and culture.
Different languages = different search intents, even for the same topic.
hreflang tags help Google understand which version of a page to show users in different regions.
Domain structure matters (e.g., ccTLDs, subdirectories, subdomains) for targeting languages and locations.
Google ranks pages separately based on the language match, not just content quality.
User behavior and click-through rates can vary by region and language, affecting rankings.
Creating dedicated pages for each language increases your chances of ranking in local search results.


